Pass Your Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate Certification Easy!
Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate Certification Exams Questions & Answers, Accurate & Verified By IT Experts
Instant Download, Free Fast Updates, 99.6% Pass Rate.

$69.99
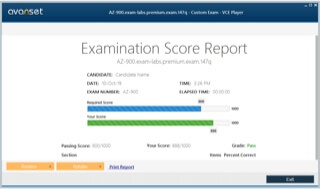
Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate Certification Exams Screenshots
Download Free Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate Practice Test Questions VCE Files
| Exam | Title | Files |
|---|---|---|
Exam AZ-500 |
Title Microsoft Azure Security Technologies |
Files 17 |
Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate Certification Exam Dumps & Practice Test Questions
Prepare with top-notch Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate certification practice test questions and answers, vce exam dumps, study guide, video training course from ExamCollection. All Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate certification exam dumps & practice test questions and answers are uploaded by users who have passed the exam themselves and formatted them into vce file format.
Microsoft Azure Security Engineer Associate – Everything You Need to Know
The Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate certification is a premier credential designed for IT professionals who want to specialize in cloud security. As organizations increasingly adopt Microsoft Azure for their cloud computing needs, the demand for security experts who can protect digital assets, manage access, and respond to threats has surged. This certification validates an individual’s ability to implement security controls, maintain identity and access solutions, and protect data, applications, and networks in Azure.
Achieving this certification demonstrates not only technical proficiency but also a deep understanding of cloud security principles. Professionals who earn this credential become essential contributors to enterprise security teams, ensuring that sensitive information remains safe while enabling organizations to leverage the full potential of cloud technologies.
Career Growth and Opportunities for Azure Security Engineers
Earning the Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate certification can significantly enhance career prospects for IT professionals. This credential validates expertise in cloud security, identity and access management, platform protection, monitoring, and compliance within Azure environments. Professionals with this certification are in high demand across industries, including finance, healthcare, technology, and government, where cloud adoption and cybersecurity are top priorities. Certified engineers can pursue roles such as cloud security specialist, identity and access management analyst, security operations center engineer, compliance analyst, or cloud security consultant.
These positions require a mix of technical knowledge, analytical skills, and strategic insight, positioning certified engineers as critical contributors to organizational security initiatives. The certification also provides tangible career benefits, including higher earning potential, enhanced professional credibility, and opportunities for advancement into senior security or cloud-focused leadership roles. Organizations increasingly seek certified professionals to design secure cloud infrastructures, enforce compliance policies, and respond proactively to emerging threats, making the credential highly valuable in today’s competitive job market.
Exam Preparation and Long-Term Success
Preparing for the AZ-500 exam requires both theoretical understanding and practical experience. Hands-on practice with Azure environments, such as configuring security features, managing identities, and implementing network protections, is essential for building confidence and proficiency. Microsoft Learn modules, online courses, official documentation, and practice labs provide structured guidance and reinforce key concepts. Beyond the exam, continuous learning and pursuing advanced certifications, such as Azure Solutions Architect Expert, Azure DevOps Engineer Expert, or globally recognized security credentials like CISSP or CCSP, can further enhance expertise and open doors to senior-level roles. In addition to technical skills, soft skills such as effective communication, problem-solving, collaboration, and analytical thinking play a crucial role in professional success. Staying current with industry trends, zero-trust architectures, AI-driven threat detection, multi-cloud security strategies, and evolving compliance regulations ensures that certified Azure Security Engineers remain adaptable and in-demand. Combining certification, practical experience, and continuous professional development allows engineers to not only secure cloud environments effectively but also shape organizational security strategies and build a long-term, rewarding career in cloud cybersecurity.
The Role of an Azure Security Engineer
An Azure Security Engineer plays a critical role in securing cloud environments. Their responsibilities span identity and access management, threat detection and mitigation, data protection, and compliance adherence. In practical terms, they work closely with cloud administrators, developers, and IT security teams to ensure the infrastructure is resilient against attacks and aligned with industry standards.
Key duties include configuring security policies, implementing firewalls, monitoring security alerts, managing encryption and identity access, and responding to security incidents. Security engineers also advise on best practices, helping organizations design secure cloud architectures from the ground up. This role requires both technical expertise and strategic thinking, as engineers must anticipate potential threats and deploy proactive security measures.
Importance of Cloud Security
Cloud computing offers scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency, but it also introduces unique security challenges. As organizations move critical workloads and sensitive data to the cloud, they become potential targets for cyberattacks. Cloud security is therefore essential to protect organizational assets, maintain trust with clients, and comply with regulatory requirements.
Azure Security Engineers address these challenges by implementing security controls tailored to cloud environments. Their work reduces vulnerabilities, prevents unauthorized access, and ensures that data and applications remain secure. The importance of cloud security cannot be overstated, as breaches can lead to financial losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences.
Skills for Long-Term Career Success
While technical knowledge is vital, soft skills are equally important for long-term career growth. Effective communication allows security engineers to explain complex security concepts to non-technical stakeholders, while problem-solving and analytical thinking are essential for investigating incidents and identifying mitigation strategies. Collaboration with IT, development, and compliance teams ensures cohesive security operations, and strategic insight helps shape organizational policies. Combining certification, hands-on experience, continuous learning, and soft skills enables Azure Security Engineers to secure cloud environments effectively, lead security initiatives, and build a sustainable, rewarding career in the dynamic field of cloud cybersecurity.
Skills Measured by the Certification
The Azure Security Engineer Associate certification validates a wide range of skills crucial for securing Azure environments. These skills include:
Identity and Access Management
Managing user identities and controlling access is a foundational aspect of cloud security. Security engineers must configure Azure Active Directory, implement multi-factor authentication, enforce conditional access policies, and manage role-based access control. These measures ensure that only authorized users can access resources and that their privileges align with organizational policies.
Platform Protection
Securing the cloud infrastructure itself is equally important. Engineers deploy network security groups, Azure firewalls, and distributed denial-of-service protection to safeguard virtual networks and endpoints. They also configure security features for virtual machines, app services, and storage accounts, ensuring that each component is fortified against potential threats.
Security Operations
Continuous monitoring and proactive threat detection are central to maintaining a secure environment. Engineers use tools like Azure Security Center and Microsoft Sentinel to detect anomalies, analyze alerts, and respond to incidents. They also perform vulnerability assessments and recommend remediation strategies, helping organizations stay ahead of evolving threats.
Data and Application Security
Protecting sensitive data and applications involves implementing encryption, access controls, and key management solutions. Engineers must classify and secure data, monitor application security, and apply best practices to prevent breaches. This ensures that both stored and in-transit data remain protected, reducing the risk of exposure.
Governance and Compliance
Compliance with industry standards and regulations is critical for organizations operating in cloud environments. Azure Security Engineers establish policies, manage audit logs, and implement security frameworks to meet regulatory requirements such as ISO, GDPR, and HIPAA. They also provide guidance on security best practices to maintain long-term governance.
Exam Overview
To earn the Azure Security Engineer Associate certification, candidates must pass Exam AZ-500: Microsoft Azure Security Technologies. The exam tests a candidate’s ability to implement identity and access solutions, secure networks and platforms, manage security operations, and protect data and applications. It evaluates both theoretical knowledge and practical skills, ensuring that certified professionals are ready to address real-world security challenges.
The exam format includes multiple-choice questions, case studies, and hands-on simulations. Candidates are expected to demonstrate proficiency in configuring security features, responding to incidents, and designing secure Azure solutions. The passing score reflects the ability to apply security principles effectively in a cloud environment.
Prerequisites and Recommended Experience
While there are no mandatory prerequisites for the certification, having prior experience in Azure administration or security is highly beneficial. Candidates should be familiar with core Azure services, virtual networks, identity management, and security tools. Practical experience with configuring security controls, monitoring environments, and responding to incidents will significantly enhance preparation for the exam.
Microsoft recommends that candidates have hands-on experience in Azure environments, complemented by formal training and study of Microsoft Learn modules specific to AZ-500. A strong understanding of cloud concepts, networking, and basic security principles provides a solid foundation for mastering advanced security techniques in Azure.
Benefits of Certification
Achieving the Azure Security Engineer Associate certification offers numerous professional and personal benefits. Certified individuals gain recognition for their expertise in cloud security, opening doors to advanced roles in IT and cybersecurity. Organizations benefit from having skilled professionals capable of safeguarding digital assets, ensuring compliance, and mitigating risks.
Key advantages of certification include career growth, higher earning potential, skill validation, and enhanced credibility. It also demonstrates a commitment to continuous learning, keeping professionals current with the latest Azure security practices and trends. As cloud adoption continues to rise, the demand for certified security engineers is expected to grow, making this certification a strategic investment in one’s career.
Recommended Preparation Tips
Effective preparation is crucial for passing Exam AZ-500 and gaining practical skills as an Azure Security Engineer. Recommended strategies include:
Hands-on practice: Engage with Azure free accounts or sandbox environments to experiment with security configurations and tools.
Official learning resources: Complete Microsoft Learn modules tailored to AZ-500 and explore official documentation for in-depth understanding.
Study groups and communities: Participate in forums and discussion groups to exchange knowledge and solve practical problems.
Practice exams: Simulate exam conditions to identify strengths and areas needing improvement.
Continuous learning: Stay updated with new Azure features, security best practices, and industry developments to maintain relevant expertise.
Career Path and Opportunities
Certification as an Azure Security Engineer Associate opens multiple career avenues in cloud security and IT. Common roles include cloud security specialist, information security analyst, security operations center engineer, and identity and access management specialist. Professionals may also transition into advanced Microsoft certifications or broader cybersecurity positions, expanding their expertise and career prospects.
The certification not only enhances employability but also equips individuals to contribute strategically to organizational security. Certified engineers help organizations design secure architectures, implement proactive defenses, and maintain regulatory compliance, making them indispensable in modern IT landscapes.
Future Trends in Cloud Security
The field of cloud security is dynamic, with evolving threats and technologies shaping the role of security engineers. Emerging trends include zero-trust architectures, automated threat detection, AI-driven security analytics, and cloud-native security solutions. Staying current with these trends is essential for professionals seeking long-term success in Azure security roles.
Microsoft continues to enhance Azure security offerings, integrating advanced tools and features to protect data, applications, and infrastructure. Azure Security Engineers must adapt to these changes, leveraging new capabilities to strengthen organizational security postures and respond effectively to evolving challenges.
The Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate certification is a valuable credential for IT professionals seeking to specialize in cloud security. It validates expertise in identity and access management, platform protection, security operations, data protection, and compliance. By earning this certification, professionals position themselves as key contributors to securing Azure environments, enhancing their career prospects and organizational impact.
The certification process combines theoretical knowledge with practical skills, ensuring that certified engineers can implement, monitor, and manage security solutions effectively. With increasing cloud adoption and sophisticated cyber threats, the demand for Azure Security Engineers continues to grow, making this certification a strategic choice for IT professionals aiming to excel in cloud security.
Identity and Access Management in Azure
Identity and access management (IAM) forms the backbone of cloud security. In Microsoft Azure, IAM ensures that the right individuals and applications have appropriate access to resources while keeping unauthorized users out. As organizations migrate workloads and data to the cloud, robust IAM practices are crucial to protecting sensitive information and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Azure provides comprehensive tools for managing identities, controlling access, and enforcing security policies. Security engineers must understand how to implement these tools effectively, balancing security needs with user productivity.
Understanding Azure Active Directory
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is Microsoft’s cloud-based identity and access management service. It serves as a central repository for user identities, applications, and devices, allowing organizations to manage authentication and authorization consistently across all cloud and on-premises resources.
Azure AD supports multiple authentication methods, including password-based logins, multifactor authentication (MFA), and passwordless options. Security engineers use Azure AD to manage users, groups, and roles, ensuring that each identity has access only to the resources required for their role.
Key features of Azure AD include:
Single sign-on (SSO) for seamless access to cloud applications.
Integration with on-premises Active Directory environments.
Conditional access policies to enforce context-aware authentication.
Identity protection mechanisms to detect and respond to suspicious activity.
By leveraging these capabilities, security engineers can reduce the risk of credential compromise and improve overall cloud security posture.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-based access control is a core principle of Azure security. RBAC allows organizations to assign permissions to users, groups, or applications based on their roles rather than granting unrestricted access. This ensures that users have only the minimum level of access necessary to perform their tasks, following the principle of least privilege.
In practice, RBAC enables security engineers to define roles such as reader, contributor, or owner for Azure resources. Custom roles can also be created to meet specific organizational requirements. By carefully assigning roles and periodically reviewing access permissions, engineers can prevent unauthorized actions and reduce the risk of accidental or malicious changes.
Conditional Access Policies and Multifactor Authentication
Conditional access policies in Azure provide an additional layer of security by enforcing access requirements based on specific conditions. These conditions may include user location, device compliance status, or application sensitivity. Conditional access ensures that access is granted only when security criteria are met, reducing exposure to threats.
Multifactor authentication is a critical component of conditional access. By requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification—such as a password and a mobile verification code—MFA mitigates the risk of unauthorized access due to compromised credentials. Security engineers configure MFA policies in conjunction with conditional access to strengthen authentication processes and enhance overall security.
Managing Identities and External Users
In addition to internal employees, organizations often need to manage external users, including contractors, partners, and customers. Azure AD provides tools for managing external identities, enabling secure collaboration while maintaining control over organizational resources.
External users can be granted access through Azure AD B2B (Business-to-Business) collaboration. Security engineers define permissions and policies for these users, ensuring that they have access only to necessary resources. Regular auditing and monitoring of external access help prevent unauthorized data exposure.
Best Practices for Securing Identities
Effective identity management requires adherence to best practices. Some key recommendations for Azure Security Engineers include:
Implement the principle of least privilege to limit access.
Enforce MFA for all users, especially privileged accounts.
Regularly review and update role assignments.
Monitor and respond to suspicious sign-in activity.
Use conditional access policies to manage access based on risk factors.
These practices help minimize the likelihood of account compromise, reduce insider threats, and improve compliance with industry regulations.
Hands-On IAM Configuration Examples
Practical experience is essential for mastering identity and access management. Security engineers often perform tasks such as:
Creating and managing Azure AD users and groups.
Configuring SSO for enterprise applications.
Implementing RBAC for subscriptions, resource groups, and individual resources.
Setting up conditional access policies and MFA for high-risk accounts.
Auditing sign-ins and reviewing security reports for anomalies.
These hands-on activities provide the skills necessary to configure and maintain secure Azure environments, directly contributing to organizational security.
Common IAM Challenges and Solutions
Implementing identity and access management can present several challenges, including:
Overprivileged accounts leading to security risks.
Misconfigured conditional access policies causing user disruptions.
Difficulty managing external user access across multiple resources.
Monitoring and detecting unusual login activity in real-time.
Security engineers address these challenges through continuous monitoring, regular policy reviews, and leveraging Azure’s built-in security tools. Automation and reporting features in Azure AD also help streamline management tasks and ensure consistent enforcement of security policies.
IAM Integration with Other Azure Security Tools
Identity and access management does not exist in isolation. It integrates with other Azure security tools to provide a comprehensive defense strategy. For example:
Azure Security Center monitors identity-related risks and provides recommendations for improvement.
Microsoft Sentinel collects logs from Azure AD to detect anomalies and generate security alerts.
Azure Key Vault works in conjunction with IAM to securely store credentials and secrets.
Integration across these tools enables security engineers to implement end-to-end security solutions that protect both identities and resources in Azure.
Benefits of Effective IAM
A well-implemented identity and access management strategy offers multiple benefits:
Enhanced security by reducing unauthorized access.
Improved user experience through single sign-on and consistent authentication.
Regulatory compliance through detailed audit logs and access controls.
Operational efficiency by automating account provisioning and policy enforcement.
Organizations that prioritize IAM create a secure, efficient, and user-friendly cloud environment, allowing teams to focus on innovation without compromising safety.
Career Relevance of IAM Skills
Proficiency in Azure IAM is highly valued in cloud security roles. Certified Azure Security Engineers with expertise in identity management can pursue positions such as cloud security specialists, identity and access management analysts, and security operations engineers. Mastery of IAM enhances career prospects by demonstrating the ability to secure critical resources and manage complex access scenarios effectively.
Identity and access management is a fundamental component of Azure security, forming the foundation for protecting cloud resources. Azure AD, RBAC, conditional access, and MFA provide a comprehensive toolkit for managing user identities and permissions securely. By adhering to best practices, performing hands-on configurations, and integrating IAM with broader security tools, Azure Security Engineers ensure that organizational assets remain safe while maintaining compliance and operational efficiency.
Effective IAM not only prevents unauthorized access but also strengthens the organization’s overall security posture, reduces risk, and enhances the credibility of the IT security team. Professionals who master IAM are well-positioned to take on advanced cloud security responsibilities and contribute meaningfully to organizational resilience in the digital era.
Platform and Network Security in Azure
Securing the underlying platform and network is a critical aspect of Azure cloud security. While identity and access management protect users and credentials, platform and network security safeguard the infrastructure itself, including virtual networks, virtual machines, storage, and applications. Azure Security Engineers are responsible for implementing a combination of preventive, detective, and responsive measures to protect resources from cyber threats.
As cloud adoption grows, organizations must ensure that their Azure environments are designed with security in mind. Platform and network security in Azure helps prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and service disruptions while maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements.
Securing Virtual Networks and Subnets
Virtual networks (VNets) are fundamental components of Azure infrastructure, providing isolated communication environments for resources. Security engineers must design VNets with segmentation, access controls, and monitoring in mind.
Subnets within VNets allow further segmentation, enabling the application of specific security policies. Network security groups (NSGs) are applied at the subnet or individual resource level to control inbound and outbound traffic. Properly configuring NSGs, routing, and firewall rules ensures that only authorized traffic reaches sensitive resources.
Additionally, Azure provides service endpoints and private links to enhance network security. Service endpoints allow secure connections between VNets and Azure services, while private links enable private access to PaaS resources without exposing them to the public internet.
Azure Firewall, Network Security Groups, and DDoS Protection
Azure offers multiple tools to protect networks from malicious activity:
Azure Firewall: A fully managed, cloud-native firewall that allows security engineers to centrally create, enforce, and log application and network connectivity policies. It supports features like threat intelligence-based filtering, stateful packet inspection, and URL filtering.
Network Security Groups (NSGs): Provide granular control over traffic to and from Azure resources, allowing the definition of rules based on IP addresses, ports, and protocols.
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Protection: Azure DDoS Protection safeguards applications against volumetric, protocol, and resource-targeted attacks. Standard DDoS protection provides real-time attack mitigation and integrates with monitoring tools to alert security teams during incidents.
By combining these tools, Azure Security Engineers can establish a layered network defense that reduces attack surfaces and improves resilience.
Security for Virtual Machines and App Services
Virtual machines (VMs) and App Services are often targets for attackers due to their direct exposure to the network. Security engineers must implement configurations that reduce vulnerabilities:
Enable endpoint protection and install security agents for malware detection.
Apply security baselines and patches regularly to reduce exploitable vulnerabilities.
Configure firewalls and NSGs to limit access to necessary ports and protocols only.
Use Azure Bastion to provide secure RDP and SSH access without exposing VMs to the public internet.
For Azure App Services, engineers must secure applications through HTTPS enforcement, managed certificates, and authentication integration with Azure AD. Continuous monitoring and vulnerability assessments help identify and remediate potential threats promptly.
Encryption and Key Management
Protecting data in transit and at rest is essential for platform security. Azure provides multiple encryption options, including:
Azure Storage Service Encryption: Automatically encrypts data at rest in storage accounts.
Azure Disk Encryption: Secures virtual machine disks using industry-standard encryption algorithms.
Azure Key Vault: Centralized storage for cryptographic keys, secrets, and certificates, allowing secure access control and auditing.
Security engineers must design encryption strategies that align with organizational compliance requirements and ensure that keys are rotated, monitored, and protected against unauthorized access.
Threat Protection Strategies in Azure
Threat protection involves identifying potential risks and mitigating them before they escalate. Azure Security Engineers use a combination of native tools and strategies, including:
Azure Security Center: Provides security posture assessments, recommendations, and threat detection across subscriptions.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud: Monitors workloads, evaluates vulnerabilities, and offers actionable remediation steps.
Microsoft Sentinel: A cloud-native SIEM solution for threat detection, investigation, and response.
By continuously monitoring alerts, analyzing logs, and implementing proactive measures, engineers can reduce the likelihood of security incidents and respond swiftly when threats arise.
Real-World Deployment Examples
Practical implementation of platform and network security includes:
Segmenting VNets for web, application, and database tiers with strict NSG rules.
Deploying Azure Firewall to filter traffic between VNets and internet-facing endpoints.
Enabling DDoS Protection for mission-critical applications, ensuring high availability during attacks.
Integrating Azure Security Center with Sentinel to correlate alerts and trigger automated responses.
Encrypting VM disks and storage accounts using Key Vault-managed keys to meet compliance requirements.
Hands-on deployment of these strategies allows security engineers to build resilient and compliant cloud infrastructures.
Best Practices for Platform and Network Security
Adhering to best practices helps minimize risks and ensures consistent security across Azure resources:
Design VNets and subnets with security segmentation in mind.
Apply NSGs, firewalls, and DDoS protection consistently across all resources.
Encrypt data at rest and in transit using managed keys.
Regularly review security recommendations and implement patches promptly.
Integrate security monitoring and incident response tools for real-time visibility.
Following these practices strengthens security, reduces attack surfaces, and ensures compliance with regulatory and organizational policies.
Challenges and Solutions in Network Security
Platform and network security comes with challenges such as:
Misconfigured network rules exposing resources to unauthorized access.
Inconsistent patch management increasing vulnerability risk.
Difficulty monitoring and correlating alerts across multiple services.
Managing security for hybrid or multi-cloud environments.
Solutions include automating security policy enforcement, conducting regular audits, using centralized monitoring tools, and applying role-based access controls for administrators. These approaches help maintain a robust and manageable security posture.
Integration with Other Azure Security Services
Platform and network security integrates with other Azure security tools to provide a holistic defense:
Identity and Access Management: Ensures that only authorized users can make network changes or access protected resources.
Threat Intelligence: Feeds from Azure Security Center inform firewall rules and NSG configurations.
Monitoring and Logging: Integration with Microsoft Sentinel allows correlation of network events with identity and access data for proactive threat response.
Platform and network security are essential components of Azure security. By implementing secure virtual networks, firewalls, NSGs, DDoS protection, VM and application security, encryption, and threat monitoring, Azure Security Engineers safeguard organizational assets and reduce the likelihood of cyber incidents.
Adhering to best practices, performing hands-on deployments, and integrating security tools across the environment ensures a resilient and compliant infrastructure. Mastery of platform and network security equips professionals to protect critical resources, support compliance requirements, and respond effectively to evolving threats in Azure.
Monitoring, Security Operations, and Compliance in Azure
In modern cloud environments, security is not only about implementing controls but also about continuously monitoring systems, responding to threats, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Azure Security Engineers play a pivotal role in maintaining operational security by leveraging monitoring tools, managing security operations, and enforcing compliance measures across an organization’s cloud infrastructure.
Effective monitoring and security operations allow organizations to detect anomalies early, respond to incidents efficiently, and minimize the impact of cyber threats. At the same time, compliance ensures that cloud deployments meet industry and regulatory standards, which is critical for avoiding legal penalties and maintaining customer trust.
Using Azure Security Center
Azure Security Center is a comprehensive tool that provides visibility into the security posture of Azure resources. It offers recommendations, threat detection, and continuous monitoring to help engineers identify vulnerabilities and mitigate risks before they can be exploited.
Key features of Azure Security Center include:
Security posture management: Evaluates resources and provides actionable recommendations to strengthen security.
Threat protection: Detects suspicious activities across virtual machines, storage, and network resources.
Compliance monitoring: Assesses Azure resources against industry standards and regulatory requirements.
Integration with other Azure services: Works alongside Microsoft Sentinel, Key Vault, and other tools for holistic security management.
Security engineers rely on Azure Security Center to prioritize risks, implement mitigation strategies, and track improvements over time. Its centralized dashboard makes it easier to manage multiple subscriptions and ensure consistent security policies across the organization.
Leveraging Microsoft Sentinel for Threat Detection
Microsoft Sentinel is a cloud-native security information and event management (SIEM) solution that provides intelligent threat detection, investigation, and response. It collects data from multiple sources, including Azure resources, on-premises systems, and third-party services, and analyzes it to identify suspicious patterns.
Benefits of using Microsoft Sentinel include:
Real-time threat detection: Identifies potential breaches and suspicious activities quickly.
Automated incident response: Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) capabilities allow engineers to automate remediation tasks.
Advanced analytics: Machine learning models and built-in analytics rules help detect anomalies that might go unnoticed.
Integration with Azure services: Works seamlessly with Security Center, Log Analytics, and other Azure tools for comprehensive monitoring.
By using Microsoft Sentinel, Azure Security Engineers can gain deeper insights into security events, respond faster to incidents, and reduce the workload associated with manual monitoring.
Monitoring Security Alerts and Incidents
Proactive monitoring is critical to identifying security threats before they escalate. Security engineers configure alerts for key metrics, such as failed login attempts, unusual network traffic, or changes to critical configurations. These alerts help detect potential breaches, insider threats, or misconfigurations that could compromise security.
Once an alert is triggered, engineers investigate the incident by analyzing logs, reviewing audit trails, and correlating events across systems. Prompt detection and investigation reduce downtime, minimize data loss, and protect organizational assets.
Incident Response Strategies
Incident response is a structured approach to managing security events effectively. Azure Security Engineers implement incident response plans that include:
Preparation: Establishing policies, defining roles, and setting up monitoring tools.
Detection and analysis: Identifying incidents and assessing their scope and impact.
Containment: Isolating affected systems to prevent further damage.
Eradication and recovery: Removing threats and restoring systems to secure states.
Post-incident review: Analyzing the response process to improve future readiness.
A well-defined incident response strategy ensures that organizations can respond swiftly and effectively, minimizing operational disruption and maintaining business continuity.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with industry regulations and standards is an essential aspect of cloud security. Azure Security Engineers implement governance and security policies to meet requirements such as:
ISO 27001: International standard for information security management systems.
GDPR: European data protection regulation focusing on privacy and personal data security.
HIPAA: U.S. regulation for protecting health information.
NIST frameworks: Guidelines for security controls and risk management.
Compliance involves continuous auditing, documentation, and reporting to ensure that all systems adhere to defined security standards. Azure provides tools like Policy and Blueprints to automate compliance management and track adherence across resources.
Governance Policies and Audit Logs
Effective governance ensures that security policies are consistently applied across Azure environments. Engineers use Azure Policy to define rules for resource configurations, access controls, and data handling. Policies can enforce encryption, restrict public access, or require tagging for compliance reporting.
Audit logs provide a detailed record of activities within Azure, including user actions, configuration changes, and access events. Reviewing these logs regularly helps detect anomalies, supports compliance audits, and provides forensic data in the event of a security incident.
Integrating Security Operations with Organizational Practices
Security operations should not exist in isolation. Azure Security Engineers collaborate with IT teams, developers, and management to align security practices with organizational objectives. Integration includes:
Coordinating incident response procedures with IT and operations teams.
Sharing security insights to guide application development and deployment.
Implementing monitoring and logging practices across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Establishing metrics and reporting frameworks for management and stakeholders.
Collaboration ensures that security measures are practical, comprehensive, and aligned with business needs.
Best Practices for Monitoring and Security Operations
Following best practices helps maintain a secure and compliant Azure environment:
Implement continuous monitoring across all resources.
Use automated alerting and incident response workflows.
Regularly review and update compliance policies and security controls.
Conduct periodic audits and risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities.
Provide training and awareness programs for teams on security and compliance requirements.
These practices enable organizations to detect threats early, respond effectively, and maintain a robust security posture.
Challenges in Security Operations and Compliance
Security operations and compliance management come with several challenges:
Volume and complexity of security alerts can overwhelm teams.
Rapidly changing cloud environments require constant updates to policies and monitoring configurations.
Ensuring compliance across multiple regulatory frameworks can be complicated.
Coordinating response across different teams and departments can lead to delays.
Solutions involve leveraging automation, centralized monitoring, and clear communication protocols. Using Azure-native tools like Security Center, Sentinel, and Policy helps manage complexity while maintaining operational efficiency.
Benefits of Effective Security Operations
Effective monitoring and security operations provide multiple benefits:
Early detection and mitigation of security threats.
Reduced impact of incidents through structured response procedures.
Compliance with regulatory and industry standards.
Improved organizational trust and credibility.
Enhanced visibility into security posture and operational risks.
Organizations that invest in robust monitoring, security operations, and compliance management are better equipped to protect their digital assets and maintain long-term business resilience.
Monitoring, security operations, and compliance are critical aspects of Azure cloud security. By leveraging tools like Azure Security Center and Microsoft Sentinel, implementing incident response strategies, enforcing governance policies, and ensuring regulatory compliance, Azure Security Engineers safeguard organizational assets while maintaining operational efficiency.
Integrating these practices into organizational processes ensures that security is proactive rather than reactive. Professionals skilled in security operations and compliance management are essential for protecting cloud environments, reducing risks, and supporting strategic business goals in the era of digital transformation.
Career Growth, Exam Preparation, and Future Opportunities for Azure Security Engineers
Earning the Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate certification is a major milestone for IT professionals focusing on cloud security. Beyond demonstrating technical skills, this certification unlocks career opportunities, increases earning potential, and positions professionals as key contributors to organizational security strategies. Understanding career paths, preparation strategies, and long-term opportunities is essential to maximize the value of this credential.
Career Advantages of the Certification
The Azure Security Engineer Associate certification provides several professional benefits:
Enhanced credibility as a verified Azure security professional.
Career advancement opportunities into senior security or cloud roles.
Competitive salaries reflecting specialized expertise.
Access to specialized roles such as cloud security specialist, identity and access management analyst, and security operations center engineer.
Recognition for practical experience in securing cloud environments.
Organizations increasingly require certified professionals to secure cloud workloads and maintain compliance, making Azure Security Engineers highly sought after across multiple industries.
Job Roles and Responsibilities
Certified Azure Security Engineers may pursue a variety of roles with specific responsibilities:
Cloud Security Specialist: Designs and implements cloud security solutions, monitors for threats, and develops policies for secure operations.
Identity and Access Management Analyst: Manages user identities, enforces access controls, and monitors authentication events.
Security Operations Center Engineer: Monitors alerts, investigates incidents, and coordinates responses across cloud and on-premises systems.
Compliance and Governance Analyst: Ensures cloud resources meet regulatory requirements, implements policies, and conducts audits.
Cloud Security Consultant: Advises on secure cloud architecture, risk management, and strategic security planning.
These roles require technical expertise, analytical thinking, and strategic insight, making certified professionals vital for organizational security.
Exam Preparation Strategies
Passing Exam AZ-500 requires both theoretical knowledge and practical experience. Recommended strategies include:
Hands-on practice with Azure sandbox environments to configure security features and simulate incidents.
Completing Microsoft Learn modules for AZ-500 to gain structured knowledge.
Breaking down exam objectives into manageable sections and focusing on areas of weakness.
Using practice exams to assess readiness and familiarize with question formats.
Engaging with online forums and study groups to exchange knowledge and learn from real-world scenarios.
Combining hands-on practice with structured study ensures readiness for both theoretical questions and practical scenarios.
Recommended Study Resources
Candidates can benefit from a variety of study resources:
Microsoft Learn AZ-500 modules for interactive tutorials and labs.
Official Azure documentation for detailed guides and best practices.
Online courses and video tutorials offering structured learning paths.
Books and eBooks focusing on Azure security technologies, networking, and compliance.
Practice labs simulating real-world Azure environments for hands-on experience.
Using a mix of these resources enhances knowledge, reinforces practical skills, and builds confidence for the exam.
Continuing Education and Advanced Certifications
After earning the Azure Security Engineer Associate certification, professionals can pursue advanced certifications:
Microsoft Certified: Azure Solutions Architect Expert for designing and implementing secure, scalable Azure solutions.
Microsoft Certified: Azure DevOps Engineer Expert for integrating security into development and operations workflows.
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) for senior cybersecurity roles.
Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) for advanced cloud security architecture and governance expertise.
Continuing education keeps professionals updated on cloud technologies, emerging security practices, and compliance requirements, paving the way for leadership and expert-level roles.
Industry Trends and Future Opportunities
The demand for Azure Security Engineers continues to rise due to increased cloud adoption, remote work, and sophisticated cyber threats. Key trends shaping the field include:
Zero-trust architectures requiring verification of every user and device before granting access.
AI and machine learning for automated threat detection and predictive analytics.
Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud environments requiring consistent security management.
Evolving regulatory frameworks driving compliance requirements.
Automation and orchestration to streamline security operations and incident response.
These trends offer opportunities for specialization, leadership, and strategic roles in cloud security.
Salary Expectations and Market Demand
Certified Azure Security Engineers are in high demand globally. Salaries vary by experience, location, and organization, but certified professionals generally earn above-average compensation. Their combination of technical expertise, hands-on experience, and certification credibility makes them highly valued by employers.
Soft Skills and Professional Development
In addition to technical skills, soft skills are essential for success:
Communication skills for explaining security concepts to non-technical stakeholders.
Problem-solving for investigating incidents and identifying effective solutions.
Collaboration with IT, development, and compliance teams to implement cohesive security measures.
Analytical thinking for assessing risks, interpreting logs, and making informed security decisions.
Developing these skills enhances professional effectiveness and career progression.
Preparing for Long-Term Career Success
To maximize the benefits of the certification:
Maintain hands-on experience with Azure services to reinforce skills.
Stay updated with security advisories, Azure updates, and emerging threats.
Participate in professional communities, conferences, and webinars.
Explore leadership opportunities in security operations, governance, or cloud architecture.
Pursue complementary certifications to broaden expertise and career options.
The Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate certification is more than an exam credential; it is a gateway to a thriving career in cloud security. Mastery of identity and access management, platform and network security, monitoring, compliance, and threat response positions professionals as critical contributors to organizational security.
Certification enhances credibility, opens doors to advanced roles, improves earning potential, and ensures professionals remain at the forefront of cloud security. Combining technical expertise, continuous learning, and soft skills enables long-term career growth, making certified Azure Security Engineers invaluable in protecting digital assets, driving innovation, and shaping the future of secure cloud computing.
Conclusion
The Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate certification equips IT professionals with the knowledge and skills needed to secure Azure environments effectively. From identity and access management to platform and network security, monitoring, and compliance, certified engineers play a vital role in protecting organizational assets and maintaining regulatory standards. Achieving this certification not only validates technical expertise but also opens doors to a wide range of career opportunities, enhances professional credibility, and increases earning potential.
Continuous learning, hands-on experience, and development of soft skills such as communication, problem-solving, and collaboration are essential for long-term success. By staying current with industry trends, leveraging Azure security tools, and pursuing advanced certifications, professionals can advance into senior roles and strategic positions within cloud security. Ultimately, the Azure Security Engineer Associate certification empowers individuals to make a meaningful impact in the ever-evolving field of cloud cybersecurity while building a rewarding and sustainable career.
ExamCollection provides the complete prep materials in vce files format which include Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate certification exam dumps, practice test questions and answers, video training course and study guide which help the exam candidates to pass the exams quickly. Fast updates to Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate certification exam dumps, practice test questions and accurate answers vce verified by industry experts are taken from the latest pool of questions.
Microsoft Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate Video Courses

Top Microsoft Certification Exams
- AZ-104
- DP-700
- AI-900
- AI-102
- AZ-305
- PL-300
- MD-102
- AZ-900
- AZ-500
- SC-200
- SC-300
- MS-102
- AZ-204
- SC-401
- DP-600
- SC-100
- AZ-700
- PL-200
- AZ-400
- AZ-800
- AZ-140
- SC-900
- PL-400
- AZ-801
- PL-600
- MS-900
- DP-300
- MS-700
- MB-280
- GH-300
- PL-900
- MB-800
- MB-330
- MB-310
- DP-100
- DP-900
- MB-820
- MB-230
- MS-721
- MB-700
- GH-900
- GH-200
- MB-920
- MB-910
- PL-500
- MB-500
- MB-335
- GH-500
- DP-420
- GH-100
- MB-240
- AZ-120
- SC-400
- DP-203
- AZ-303
- MO-100
- MB-210
- 98-388
- MB-900
- 62-193
- 98-383
Site Search: