- Home
- Popular IT Certifications
- How To Configure and Verify DHCP (IOS Router)
Describe the process of Configuring and verifying DHCP (IOS Router)
(DHCP) is a system protocol that empowers a server to consequently relegate an IP location to a machine from a characterized scope of numbers (i.e., a degree) designed for a given system.
DHCP relegates an IP address when a framework is begun, for instance:
- A client turns on a machine with a DHCP customer.
- The customer machine sends a show solicitation (called a DISCOVER or DHCPDISCOVER), searching for a DHCP server to reply.
- The switch controls the DISCOVER bundle to the right DHCP server.
The server gets the DISCOVER parcel. In light of accessibility and use strategies set on the server, the server decides a proper location (if any) to provide for the customer. The server then briefly saves that address for the customer and sends again to the customer an OFFER (or DHCPOFFER) parcel, with that address data. The server additionally arranges the customer's DNS servers, WINS servers, NTP servers, and in some cases different administrations too. The customer sends a REQUEST (or DHCPREQUEST) bundle, telling the server that it expects to utilize the location.
The server sends an ACK (or DHCPACK) bundle, affirming that the customer has been given a lease on the location for a server-determined time of time. At the point when a machine utilizes a static IP address, it implies that the machine is physically arranged to utilize a particular IP address. One issue with static task, which can come about because of client mistake or mindlessness to detail, happens when two machines are arranged with the same IP address. This makes a clash that brings about loss of administration. Utilizing DHCP to alertly dole out IP locations minimizes these clashes.
Element Host Configuration Protocol is utilized by machines for asking for Internet Protocol parameters, for example, an IP address from a system server. The protocol works focused around the customer server model. DHCP is exceptionally normal in all cutting edge networks extending in size from home systems to substantial yard systems and local Internet administration supplier systems. Most private system switches get a comprehensively exceptional IP address inside the supplier system. Inside a nearby system, DHCP allots a neighborhood IP location to gadgets joined with the nearby system.
At the point when a machine or other arranged gadget join with a system, its DHCP customer programming in the working framework sends a show question asking for essential data. Any DHCP server on the system may benefit the appeal. The DHCP server deals with a pool of IP addresses and data about customer arrangement parameters, for example, default portal, space name, the name servers, and time servers. On accepting an ask for, the server may react with particular data for every customer, as long ago designed by a director, or with a particular location and some other data substantial for the whole system, and the time period for which the portion (lease) is legitimate. A host regularly inquires for this data instantly in the wake of booting, and intermittently from there on before the termination of the data. At the point when a task is invigorated by the customer machine, it at first demands the same parameter values yet may be doled out another location from the server, in view of the task arrangements set by heads.
On huge systems that comprise of different connections, a solitary DHCP server may benefit the whole system when helped by DHCP transfer executors spotted on the interconnecting switches. Such executors transfer messages between DHCP customers and DHCP servers placed on diverse subnets. Contingent upon execution, the DHCP server may have three systems for assigning IP-addresses:
- Dynamic allotment: A system head holds a scope of IP locations for DHCP, and every customer machine on the LAN is designed to ask for an IP address from the DHCP server amid system instatement. The solicitation and-award procedure utilizes a lease idea with a controllable time period, permitting the DHCP server to recover (and after that reallocate) IP addresses that are not reestablished.
- Programmed designation: The DHCP server forever allots an IP location to an asking for customer from the extent characterized by the head. This is similar to element portion, yet the DHCP server keeps a table of past IP address assignments, so it can specially appoint to a customer the same IP address that the customer beforehand had.
- Static distribution: The DHCP server apportions an IP location focused around a preconfigured mapping to each customer's MAC address. This peculiarity is differently called static DHCP task by DD-WRT, settled address by the DHCPD documentation, address reservation by Net gear, DHCP reservation or static DHCP by Cisco and Linksys, and IP address reservation or MAC/IP location compulsory by different other switch producers.
DHCP is utilized for Internet Protocol form 4 (Ipv4), and Ipv6. While both adaptations fill the same need, the points of interest of the protocol for Ipv4 and Ipv6 are sufficiently diverse that they may be viewed as independent protocols. For Ipv6 operation, gadgets might then again utilize stateless location auto configuration. Ipv4 hosts might additionally utilize join neighborhood tending to accomplish operation limited to the nearby system link. DHCP was initially characterized as a guidelines track protocol in RFC 1531 in October 1993, as an augmentation to the Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP). The inspiration for augmenting BOOTP was that BOOTP obliged manual intercession to include setup data for every customer, and did not give a system to recovering unused IP addresses. DHCP improvement finished in RFC 2131 in 1997 and stays starting 2014 the standard for Ipv4 systems. DHCPv6 is archived in RFC 3315. RFC 3633 included a DHCPv6 component for prefix assignment. DHCPv6 was further stretched out to give design data to customers arranged utilizing stateless location auto configuration as a part of RFC 3736. The BOOTP protocol itself was initially characterized in RFC 951 as a substitution for the Reverse Address Resolution.
Configuring router interfaces to use DHCP
The DHCPprotocol utilizes a connectionless administration model, utilizing the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). It is actualized with two UDP port numbers for its operations which are the same concerning the BOOTP protocol. UDP port number 67 is the terminus port of a server, and UDP port number 68 is utilized by the customer.
DHCP operations fall into four stages: server disclosure, IP lease offer, IP solicitation, and IP lease affirmation. These stages are frequently abridged as DORA for disclosure, offer, appeal, and affirmation.
The DHCPprotocol operation starts with customer's television an appeal. In the event that the customer and server are on distinctive subnets, a DHCP Helper or DHCP Relay Agent may be utilized. Customers asking for reestablishment of a current lease may convey straightforwardly by means of UDP unicast, since the customer as of now has a secured IP addressed at that point. The customer shows messages on the system subnet utilizing the objective address 255.255.255.255 or the particular subnet telecast address. A DHCP customer might additionally ask for its last-known IP address. In the event that the customer stays associated with the same system, the server may allow the appeal. Else, it depends whether the server is situated up as definitive or not. A definitive server denies the appeal, creating the customer to issue another solicitation. A non-definitive server essentially disregards the appeal, prompting an execution subordinate timeout for the customer to lapse the solicitation and request another IP address.The Cisco IOS DHCP Server peculiarity is a full DHCP Server execution that appoints and oversees IP addresses from pointed out location pools inside the switch to DHCP customers. On the off chance that the Cisco IOS DHCP Server can't fulfill a DHCP demand from it database, it can forward the appeal to one or more optional DHCP Servers characterized by the system chairman.
Figure demonstrates the essential steps that happen when a DHCP customer asks for an IP address from a DHCP Server. The customer, Host A, sends a DHCPDISCOVER show message to spot a Cisco IOS DHCP Server. A DHCP Server offers arrangement parameters, (for example, an IP address, a MAC address, an area name, and a lease for the IP location) to the customer in a DHCPOFFER unicast message.


DHCP options (Basic overview and functionality)
At the point when a DHCP server gets a DHCPDISCOVER message from a customer, which is an IP location lease ask for, the server saves an IP address for the customer and makes a lease offer by sending a DHCPOFFER message to the customer. This message contains the customer's MAC address, the IP address that the server is putting forth, the subnet veil, the lease length of time, and the IP location of the DHCP server making the offer.
The server decides the design focused around the customer's fittings address as determined in the CHADDR (customer equipment location) field. Here the server, 192.168.1.1, tags the customer's IP address in the YIADDR (your IP address) field.in reaction to the DHCP offer, the customer answers with a DHCP appeal, telecast to the server, asking for the offered location. A customer can get DHCP offers from various servers, yet it will acknowledge one and only DHCP offer. In view of obliged server recognizable proof choice in the solicitation and show informing, servers are educated whose offer the customer has accepted. When other DHCP servers get this message, they withdraw any offers that they may have made to the customer and give back where its due location to the pool of accessible addresses. When the DHCP server gets the DHCPREQUEST message from the customer, the design methodology enters its last stage. The acknowledgement stage includes sending a DHCPACK parcel to the customer. This bundle incorporates the lease length of time and whatever other setup data that the customer may have asked. As of right now, the IP setup procedure is finished.
The protocol anticipates that the DHCP customer will arrange its system interface with the arranged parameters. After the customer gets an IP address, the customer may utilize the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) to counteract location clashes created by covering location pools of DHCPservers. ADHCP customer may ask for more data than the server sent with the first DHCPOFFER. The customer might likewise ask for rehash information for a specific application. Case in point, programs use DHCP Inform to acquire web substitute settings by means of WPAD. The customer sends an appeal to the DHCP server to discharge the DHCP data and the customer deactivates its IP address. As customer gadgets generally don't know when clients may unplug them from the system, the protocol does not order the sending of DHCPRelease. ADHCP server can give discretionary design parameters to the customer. RFC 2132 portrays the accessible DHCP alternatives characterized by Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) -DHCP and BOOTP Parameters.A DHCP customer can choose, control and overwrite parameters gave by a DHCP server.
Excluded addresses
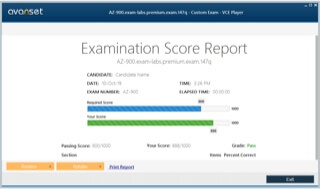
If you take this picture as example;

Now that's how it's done;

Lease time
In the wake of setting the location ranges for a degree, you can screen and confirm the rents that come about because of DHCP assignments. While there is no restriction to the quantity of rents that you can arrange for every extension, on the off chance that you have unified with a few thousand leases, it can take Network Registrar a while to sort them. You can see the current state of leases for the degree location ranges.

Make arrangements that have perpetual rents deliberately. There is a sure measure of turnover among customers even in a nature. Versatile hosts may be included and uprooted, desktop hosts moved, and system connector cards supplanted. On the off chance that you evacuate a customer with a perpetual lease, you can't re-utilize the location until you reconfigure the server. It would be better to make a long rent, for example, six months, which guarantees that addresses are eventually recuperated without head mediation.
Like all other parts of networking, DCHP protocols are important part. So those people, who want to have future in this field, should make sure they learn about this specific protocol.
Site Search: